
It determines the present state of finances, aside from setting achievable financial goals to plan on how to achieve the said objectives. In order to do this, one must check his or her source of income, expenses, savings, investments, and insurance needs. Thus, with proper planning, you gain much clearer views regarding where you are and where you ought to go.Planned Management of Finances
Planning finances can be significant for many reasons.
A personal financial plan is your guide to good decisions and help in preventing common mistakes on your part, such as overspending or getting into unnecessary debt, or worse, not saving for any kind of future significant event, retirement, or buying a home. Financial planning will assist you in accomplishing your long-term financial goals, building wealth over time, and protect you from many common financial risks including involuntary job loss or being unable to work because of illness.
Achieve financial independence and peace of mind
Key Elements of Personal Financial Planning
In designing a well-rounded personal financial plan, the following are the key elements that you will have to put in place. All these elements will ensure proper balance and control over your money in a strategic way.
Budgeting forms the backbone of any good financial planning exercise. Without a budget you tend to lose your head of what is going on with your money and may even waste some opportunities to save or invest in something more profitable. Here’s how you can create an effective budget
List all sources of income: Whether salaried employee, having some side income, or earning passive income, list it down.
Make a list of all expenses as fixed and variable cost that applies: Rent, mortgage, utilities, groceries, entertainment, and the like.
Identify expense categories: Even your expenditures need some coming into categories-housing, transport, food, entertainment, and so on. Then, it almost becomes crystal clear where the money is going and where there is an opportunity to cut.Set spending limits: Provide every category with a spending limit after performing the same calculation working on your income and set of goals. That minimizes the chance of overdraft and saves saving money in your pocket.
2. Emergency Fund
These are savings that act as cushions, money you keep back for rainy days. It may be a medical emergency bill, a repair on your car, or even unemployment. This financial cushion keeps you from having to see debt in trying moments.
What do you need? Save at least 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses. Then, in case some form of emergency arises, you can provide your financial situation with the flexibility not to go borrowing from credit cards or loans just to get through.
Where should it be? A no-risk, liquid account should be positioned within easy reach of a high-yield savings account so that it can be accessed very easily, and quickly.
3. Debt Management
Face it: debt tends to surprise people pretty quickly and can be a huge obstacle toward the goal of getting financially stable. And if you have revolving loans or credit cards floating around out there, get a plan together to eliminate those debts.
High-interest debt: your high-interest debt, like credit card balances, so pay those guys off first Personal Financial Planning.
Debt snowball or avalanche method to pay out debts: It can also be done by the snowball method, where the smallest of debts are attended first, or by the avalanche method, where the highest-interest debt is paid first. Whatever is your choice, this will surely do much in making the debt-reduction process systematic.
Don’t continue to incur new debt: After the process pays you out on this accumulated debt then there should be no more incurred new high-interest debt piled and, tracking expenses, living on your budget.
Save for the Future Personal Financial Planning
Saving and investing in oneself is yet another great activity for long-term wealth building. The sooner you start saving and, more importantly, investing, the more time your money will have to grow with a little help from compounding interest. Here are some very smart saving and investing principles for you:
4. Types of Investments
The investment would depend on the risk level. They can vary from a high-risk and a high-reward type to a low-risk and a low reward investment vehicle. Some of the most popular mainstream investment tools include:
Stocks: Any time you buy shares you are buying equity to the company’s share. This usually earns more, but it gives investors more volatility and risk.
Bonds: These are debt papers issued either by the government or companies. They carry relatively low risk but repays lesser amounts to investors.
Real Estate: One gains passive income as well as long-term capital appreciation though such investment does command a lot of capital and bears more front-end cost.
Index Funds and ETFs: Normally, they track the market index and hence the performance of the very same market index, say, the S&P 500. Diversification and lower fees than actively managed funds are provided
5. Retirement Planning
Retire. Much personal financial planning goes to retirement. Saving big to retreat early and save for retirement really adds up to a very large number that will secure your old age.
Retirement Accounts: Always contribute to retirement accounts such as Roth IRA, Traditional IRA, or the 401 (K). These are retirement plans with tax advantages and meant for long term objectives- that is retirement.
Employment-Based Plans.If you are in a work-sponsored retirement plan, try contributing as the maximum as you can since your employer may match some of your contributions.
The Earlier, the Better: The longer you begin saving for retirement, the more time your money will have to grow. Contribute as often as possible and with whatever you can muster.
Tax Planning
Tend to cost so much that you take out so much money from accounts, so leave some room for taxes while formulating your financial plan. Here are the most appropriate ways to save taxes:
6. Tax-Efficient Strategies
Tax-Deferred Accounts: Invest in a tax-deferred retirement account, like 401(k) or Traditional IRA, which reduces your near-term taxable income.
Tax-Free Accounts: Fund a Roth IRA with dollars after tax; distributions are tax-free in retirement.
Tax-Loss Harvesting: Offset taxable income by selling investments representing less money-money for which you count toward capital losses.
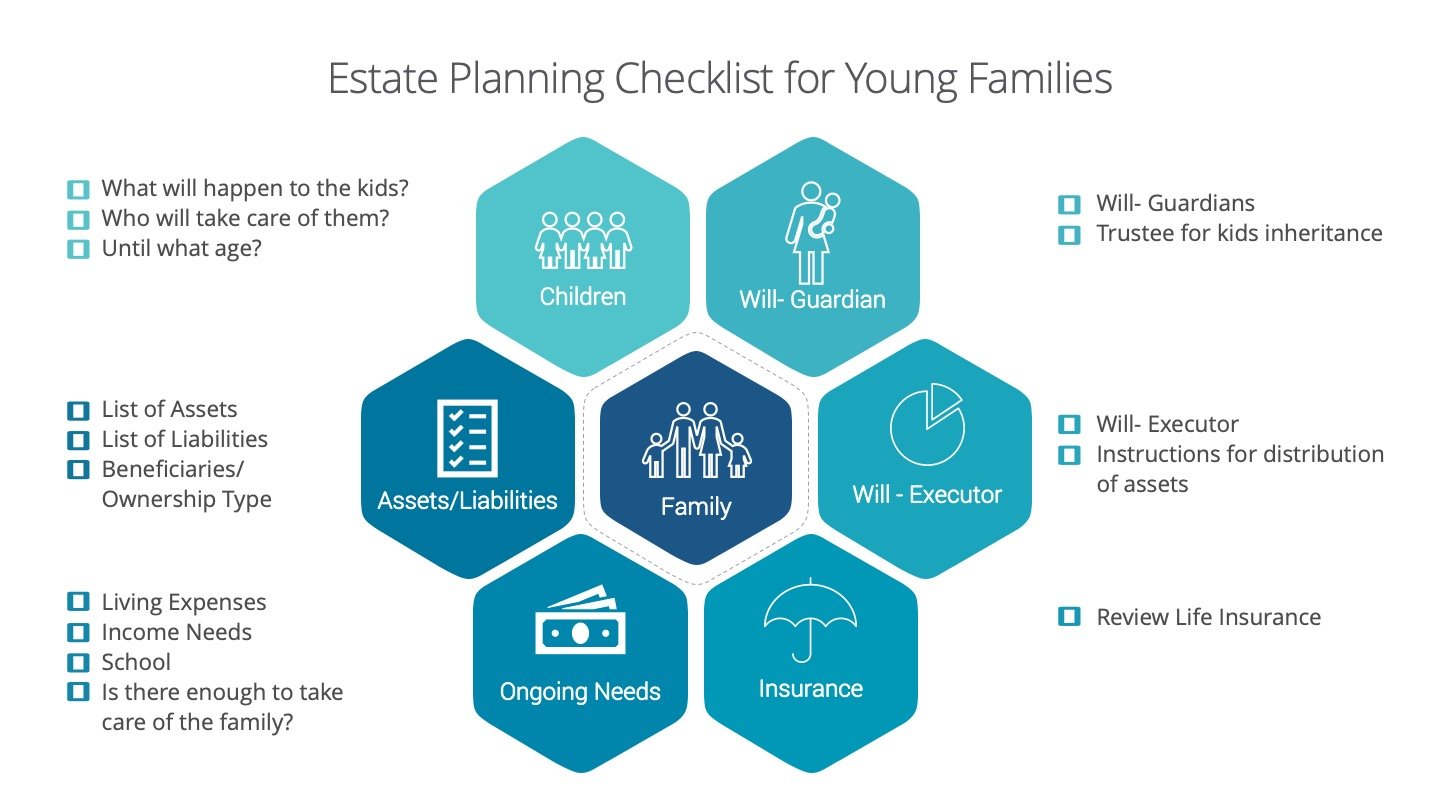
7. Estate Planning
Estate planning makes it possible to have your property transfer upon your passing in the manner of your choice. Not, perhaps, the most popular subject of conversation for most people, but it is a part of financial planning.
Will: It is a legal document that outlines what you want in regards to the division of your estate and property at or on your death.
Trust: Also allows you to have a form of control over your assets while you are living. It also spells out during how, while you live, your assets will be dispensed after your death. A trust most times avoids probate.
Power of Attorney and Healthcare Proxy: This will determine who will take care of your finances or your healthcare when you might not be in a position to.
8. Risk Management and Insurance
Insurance is one very good wealth that protects a loss of money where unforeseen problems arise, either through illness or accidents, even death.
Life Insurance: Pay out your money to loved ones in the event of your death
Disability Insurance: Pay out your income in case illness or injury prevents you from working.
Home and Auto: Protect your house and cars in case they get destroyed due to an accident or auto-theft.
It’s a dynamic process that does not come to fruition without discipline and commitment. Budgeting, building an emergency fund, managing debt, responsible investing, and planning for the future will all add up towards a financial plan that brings you great hope for the realization of your goals and peace of mind in your finances. Start today and take control of your finances to build toward a secure financial future.
Take stock of your situation. Track how much you earn and spend, make a budget, and set some specific financial goals. Once you have done those things, then work on building your savings accounts, paying off any debt, and investing for the future.
This usually becomes the default move to set aside at least 15 percent of your pretax income into retirement, which should factor in any employer-matched contribution. The earlier the savings start, the better you will do in retirement.
A 401(k) typically is an employer-sponsored retirement account. In some cases, even the employer matches contributions made to it. You yourself establish a retirement account in an IRA. Both plans have tax advantages. The contribution limits though tend to be higher with a 401(k).4. How can I save more taxes?
Save and invest in tax-deferred accounts, 401(k) or Traditional IRA, allow tax-free distributions with a Roth IRA, and implement tax-loss harvesting to decrease capital gains.
You will pay high-interest debts first, usually credit cards; and you may even use the debt snowball or avalanche strategy to pay down balances systematically.6. How will I, financially take care of my loved ones?


