Blockchain technology may just be the influence which has been welcomed into the digital playground to change the ways people consider and perceive how things have been bestowed upon traditional avenues in matters of data, money, and security as known earlier. Blockchain technology is decentralized, open, and transparent and has widely adopted all sectors.
How does blockchain work and why is it revolutionary?
In this article, we will try to focus on defining the concept of Blockchain, explaining its main principles and applications, advantages and problems, and future perspective as well as a lot of other aspects related to it.
Blog Post on “Blockchain Technology Explained”
What is Blockchain Technology?
What is Blockchain?
Evolution and History of Blockchain
Characteristics of Blockchain
Understanding Blockchain’s Decentralized Nature
Security and Transparency in Blockchain
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain Structure: Blocks and Chains
How do the Transactions Get Verified and Recorded on Blockchain
Blockchain Networks
Public and private blockchain networks Blockchain network permissioned vs. permissionless Consensus Mechanism in the Blockchain Proof of Work PoW vs. Proof of Stake PoS.
Other Types of Consensus Model:
Proof of Authority (PoA) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) H3: Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Bitcoin: The First Blockchain Other forms of Cryptocurrencies and its implementation of Blockchain
H2: Blockchain Applications Blockchain Financial Service and in Banking
Blockchain for Supply Chain Management
Blockchain in Healthcare and Medical Records
H3: Blockchain for Smart Contracts What are Smart Contracts?
Apps of Smart Contracts in real life
H2: Blockchain Technology Advantage of Blockchain -Decentralization and Trust
Further security features
Lower the cost, and accelerate transactions
H2: Blockchain Technology Challenges in Blockchain Implementation Scalability and Energy Consumption by Blockchain
Legal and regulatory issues in blockchain adoption
H2: Blockchain Future Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence:
A Match Made in Heaven Blockchain and Internet of Things Web 3.0, H2:
Blockchain Frequently Asked Questions What is Blockchain Technology and How Does it work?
How does blockchain apply to Cryptocurrencies?
Can blockchain be hacked?
What are smart contracts, and how do they work?
How does blockchain function to eliminate Supply Chain Frauds?
Is blockchain the future of digital security?
H2: Conclusion Blockchain Potentiality and Impact of Technologies Industry blockchain technology-related application
What is blockchain technology?
It’s digital technology that enables safe recording of data in a networked system in the form of a distributed ledger. That result shall be proved and kept immutable. Transactions are usually kept in a “block,” and then that block ties itself to other blocks, and that are a “chain.”
That form basically ensures once data have been put down, it cannot be altered; hence blockchain is pretty secure tech.
Origins and History of Blockchain
Blockchain technology was first discovered in the year 2008. There was an anonymous person by the name Satoshi Nakamoto that published Bitcoin that is electronic or the base technology of Bitcoin, building on the concept to provide a safe mechanism of transferring value with decentralization and transparency without intermediate support. Since its discovery, blockchain has expanded to enormous applications transforming the general scope of application from mere cryptocurrencies to supply chain management, voting systems, and even health care among others.
Key Characteristics of Blockchain
Know the Decentralized Nature of Blockchain
Distributed ledger and control are special to blockchain on some central thing and not on some. All of the nodes in this architecture would have access to the full ledger as well as validate the transactions. Since by design, these systems are decentralized, they can’t have some point of failure, and hence no weak spot for an attack or fraud.
Blockchain Security and Transparency
This means that many kinds of cryptography algorithms form the basis of the security in blockchain. However, pieces of information are encrypted in a block in such a way that it won’t be impossible to change. Almost any information will not be able to change because each block is connected through a hash cryptographically secured to end up in that block of the previous block. The blockchain is always transparent because every and any transaction has been presented to all members or participants in a network. Transparency fosters trust and also accountability.
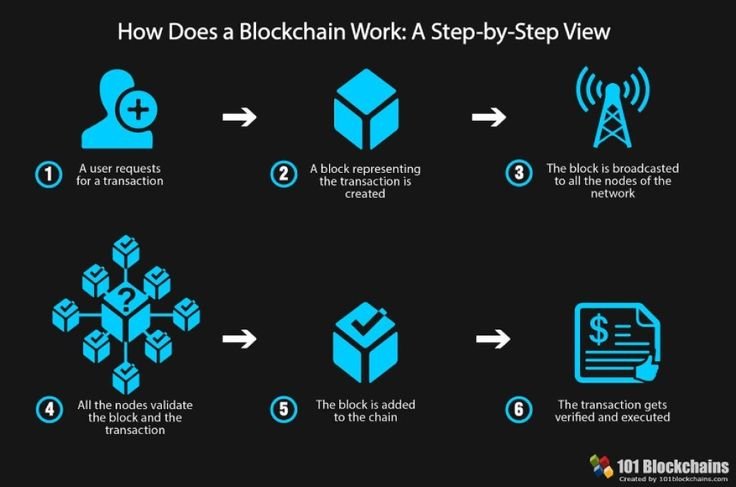
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain Structure: Blocks and Chains
Technically, speaking using the term blockchain, one refers to a sequence of “blocks” of a list of transactions. In it, a block contains information in terms of time, transactional data, and a cryptographical hash of the previous block. Then it continues without any bounds to blocks without bound wherein each new block is appended by being added to the preceding block in a way that once appended to the chain, no party will ever alter the sequence it thereby provides an immutable history of all transactions.
How Transactions are Validated and Included in the Blockchain
Apart from being validated by consensus mechanisms by miners in proof-of-work blockchain systems except for validators in proof-of-stake blockchain systems, it is broadcast to the blockchain network. Upon validation, this new block is formed except for added to the blockchain with transactions getting added with other transactions.
All the transactions are valid except for transparent .
cokies
Types of Blockchain Networks
Public vs. Private Blockchain Networks
Where public blockchain is public, any party that participates can join the network and verify transactions. Public blockchains include Bitcoins and Ethereums. Private blockchains, however are restricted to a few people. Permissioned blockchain is that which is used by organizations since they want to have control over their network while at the same time reaping the benefits of the security and transparency blockchain has to offer.
Permissioned and Permissionless Blockchain
That blockchain where entry, permission or membership of any blockchain has to be approved by a central authority or consortium is referred to as a permissioned blockchain. However, for doing so, a permissionless blockchain allows anyone to join without the requirement of approval of any individual. For example, a permissionless blockchain is that kind of public blockchain like Bitcoin and Ethereum. However, most of the blockchains are deployed within an organization that are permissioned.
Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
Proof of Work and Proof of Stake
There are two use vastly consensus mechanisms. There is a blockchain that relies on proof of work, and another one that’s based on proof of stake. In the case of proof of work, the miners will dig through some complex mathematical problems that effectively constitute an effort toward validation of the transactions so that they could append them to a blockchain. While in the latter case of proof of stake, validators actually verify transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrencies that they hold.
Except for the above, a few others, very widely accepted consensus models of other alternatives include Proof of Authority and Delegated Proof of Stake.
Apart from PoW and PoS, there are quite a few other consensus models like Proof of Authority and Delegated Proof of Stake. In the former, Proof of Authority, it would completely depend on the trusted validators whereas in the latter, DPoS, people vote on who gets to validate transactions. And then it can scale and even be efficient for certain use cases.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin:
The First Blockchain Application
Bitcoins were the first form of currencies that are actually used via blockchain, making it a decentralized asset for those users who have to send or receive digital currencies without someone controlling their central authority. Bitcoins are literally written within the blockchain network through a distributed process that is peer-to-peer in nature; hence it becomes open, safe, and unchanging pretty much a resistance against government control or censoring.
Other Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Use
Since Bitcoin, however, thousands more have popped up. Every other cryptocurrency uses blockchain in one form or another.The rise of Ethereum has introduced the concept of smart contracts to many people, which are self-fulfilling contracts containing the terms of the agreement in a few lines of computer code. Other cryptoassets, like Ripple or XRP, for example, are more oriented on enabling speedier international money transfers.
Blockchain in Financial Services and Banking
It will also disorganize financial services mainly because of lower costs of transactions, better security, and high velocity of transactions. It will also benefit the banks and other financial institutions in their rationalization of cross-border payments, loan disbursements, settlement of trade amongst others via blockchain.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Management
In this case, tremendous value will be achieved through more transparent and traceable supply chains. All parties within a network of transactions can track movement on a shared, immutable ledger called a blockchain, while freezing all frauds, errors, inefficiencies in the chain at the same time.
Blockchain in Healthcare and Medical Records
Blockchain for Smart Contracts
What is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is by its very nature self-executing by virtue of its terms having been directly codified.
Real Life Scenario:
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
честные казино с быстрыми выплатами
бездепозитные бонусы казино
играть в лучшем казино на деньги
база казино с бездепозитным бонусом
онлайн казино России
casino oyunu
Decentralization and Trust in Blockchain
It simply means decentralization. No central authority at all. Here, in this case, peers have thought of trusting the system rather than the middleman. And thus, quite a few benefits come along with that.


